2017 Road Weather Management Performance Measures Update
Chapter 5. Partnerships and Stakeholder Collaboration
OVERVIEW
Through partnerships and stakeholder collaboration, the Road Weather Management Program (RWMP) utilizes a multi-disciplinary approach to address road weather challenges. By partnering with State departments of transportation (DOT) on research projects and attending and presenting at conferences, workshops, or meetings, the RWMP strives to build partnerships that will advance road weather innovations and practices. RWMP promotes data sharing and information exchange opportunities in order to create a collaborative and comprehensive road weather program. This chapter highlights the extent to which the RWMP is fostering and encouraging effective partnerships and stakeholder collaboration.
PERFORMANCE FINDINGS
Participation in Road Weather Program Research and Development Activities
Information sharing and collaboration are fundamental to road weather management. One way RWMP is facilitating these is by partnering with State and local transportation agencies to advance various research and development (R&D) projects. Performance Measure 1 captures this information and includes initiatives such as the Pathfinder Project, the RWMP Capability Maturity Framework (CMF), the Weather Data Environment Integrated Mobile Observations (IMO) Program, vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) application development efforts, and weather responsive traffic management (WRTM) implementation support activities.
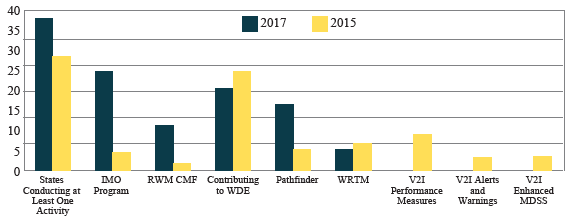 RWM = Road Weather Management. CMF = Capability Maturity Framework. IMO = Integrated Mobile Observations. MDSS = Maintenance Decision Support System. V2I = vehicle-to-infrastructure. WRTM = weather responsive traffic management. WDE = Weather Data Environment.
Figure 21. Graph. Performance Measure 1 – number of agencies participating in road weather research and development projects, 2017 vs. 2015 data.
RWM = Road Weather Management. CMF = Capability Maturity Framework. IMO = Integrated Mobile Observations. MDSS = Maintenance Decision Support System. V2I = vehicle-to-infrastructure. WRTM = weather responsive traffic management. WDE = Weather Data Environment.
Figure 21. Graph. Performance Measure 1 – number of agencies participating in road weather research and development projects, 2017 vs. 2015 data.
Of particular note are the Pathfinder and IMO Program participation levels, which increased significantly from 2015. Both are being promoted in the Weather-Savvy Roads innovation through the Every Day Counts (EDC) initiative. Pathfinder is a perfect example of the importance and efficiency of collaborative efforts. The National Weather Service (NWS), State DOTs, and support contractors work together to provide and share consistent and situation- appropriate road weather information. These partnerships then allow for better and more accurate information to be conveyed to the public on weather impacts to the transportation system. Overall, the number of States that are conducting at least one R&D activity has increased by approximately 52 percent (from 27 to 41) from the last update report.
Participation in Meteorological Assimilation Data Ingest System
Another example of fostering stakeholder collaboration and partnerships by the RWMP is supporting National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) by working with State DOTs to sign data-sharing agreements and ensure data quality by integrating quality checking algorithms into the system. Performance Measure 10 tracks the number of State DOTs that are participating in the Meteorological Assimilation Data Ingest System (MADIS) program by signing a data sharing agreement and providing real-time data to MADIS.
From 2016 to 2017, the participation of State DOTs has increased from 12 to 21, a 75 percent increase.
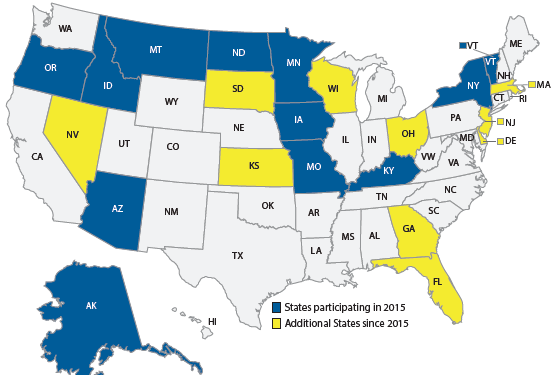 Figure 22. Map. 2017 State participation in the Meteorological Assimilation Data Ingest System (MADIS) Program
Figure 22. Map. 2017 State participation in the Meteorological Assimilation Data Ingest System (MADIS) Program.
Engagement with National Weather Service
A similar performance measure, which has also shown notable growth in RWM partnerships in recent years, tracks the number of agencies that coordinate with their local weather forecast offices for assistance in road weather management and operations (Performance Measure 18, summarized in Figure 23).
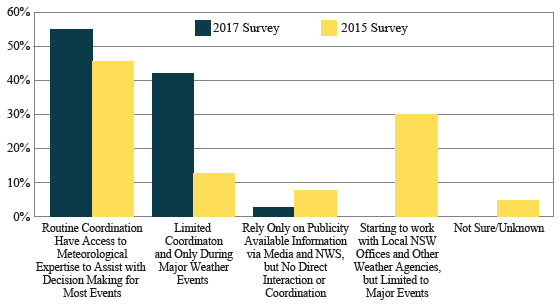 NWS = National Weather Service
Figure 23. Chart. Level of coordination between State departments of transportation and National Weather Service local forecast offices.
NWS = National Weather Service
Figure 23. Chart. Level of coordination between State departments of transportation and National Weather Service local forecast offices.
Local weather forecast information is a critical input in road weather management and operations decision-making. When a State DOT makes an effort to coordinate with its NWS local forecast
office, it reflects a commitment to enhancing the performance of road weather management and operations activities. Almost all respondents (98 percent) reported at least some coordination
with the NWS local forecast office, with 55 percent saying they routinely coordinate and have access to meteorological expertise. This represents a large increase from 2015, where one-third
of the respondents were just starting to work with the NWS.