Model Systems Engineering Documents for Central Traffic Signal Systems
Appendix F: Standardized Communications Protocol Stack Interface Diagrams
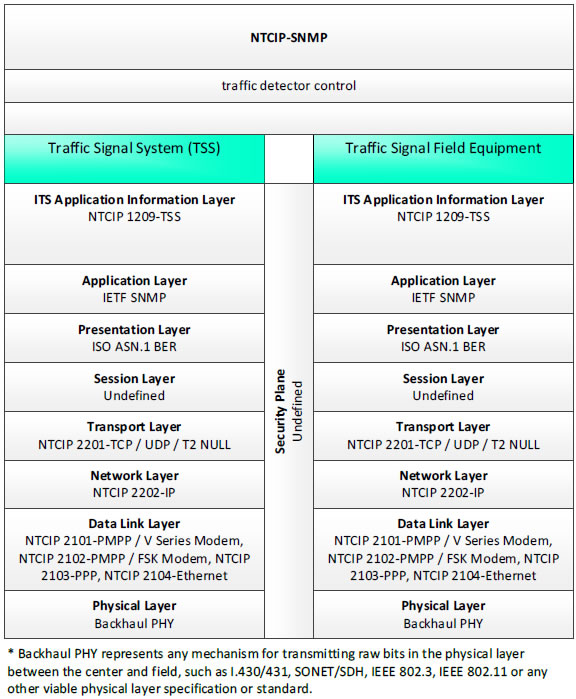
NTCIP-SNMP, traffic detector control - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1209-TSS; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plan - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1209-TSS; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2201-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 9. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-SNMP Triple of Traffic Signal System → traffic detector control → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
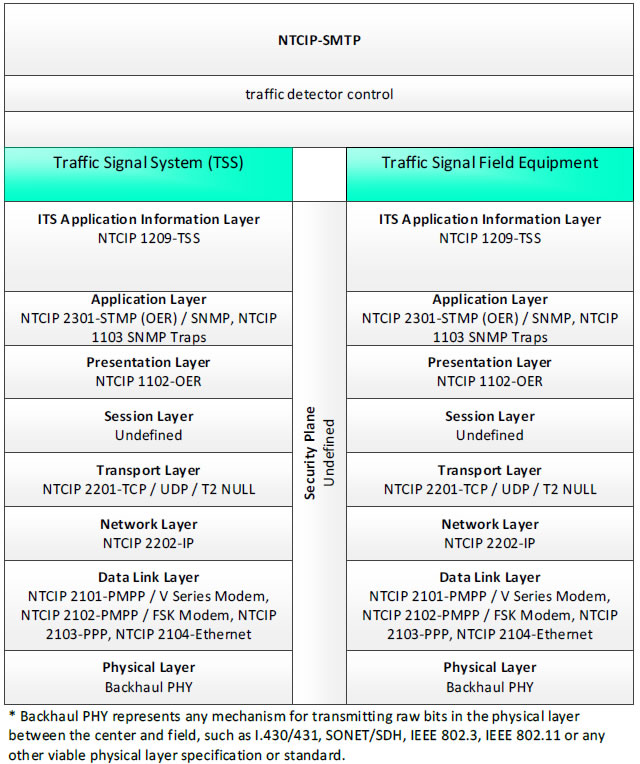
NTCIP-SMTP, traffic detector control - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1209-TSS; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plan - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1209-TSS; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 10. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-STMP Triple of Traffic Signal System → traffic detector control → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
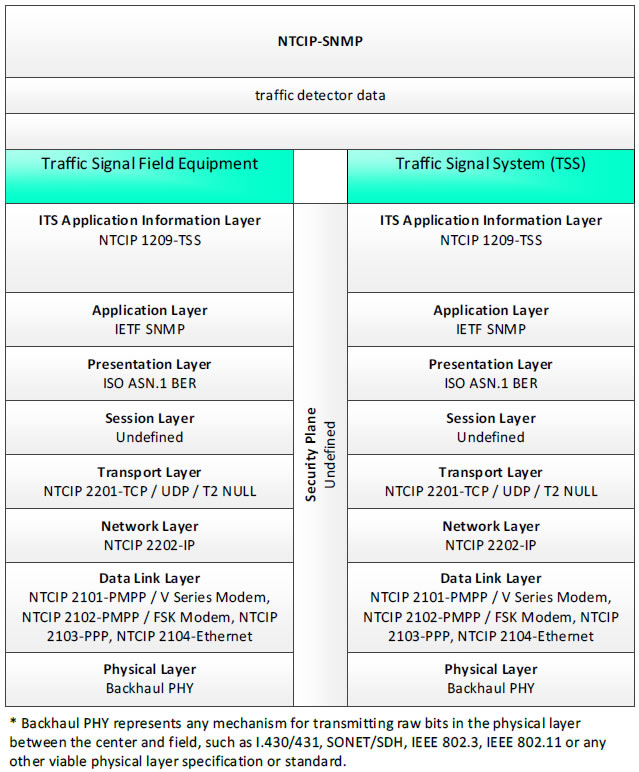
NTCIP-SNMP, traffic detector data - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1209-TSS; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plan - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1209-TSS; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY;* Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 11. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-SNMP Triple of Traffic Signal Field Equipment → traffic detector data → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
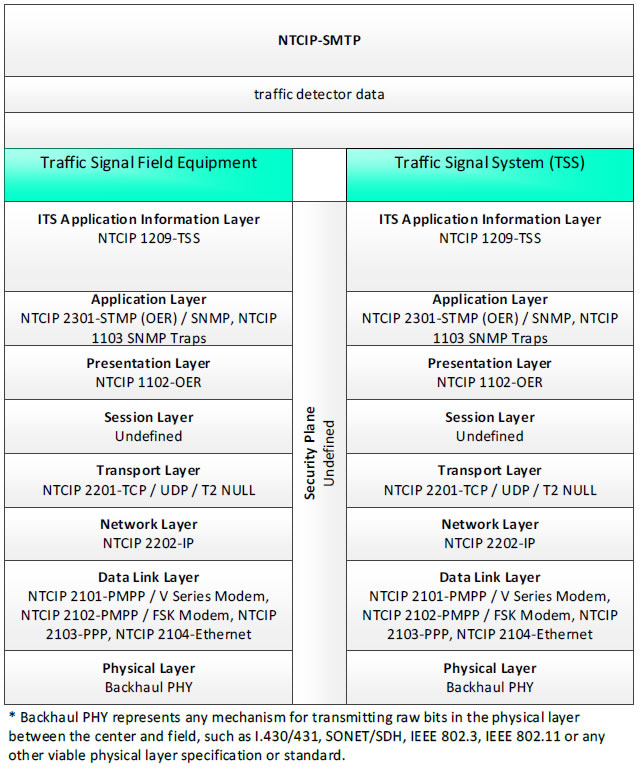
NTCIP-SMTP, traffic detector data - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1209-TSS; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plan - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1209-TSS; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 12. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-STMP Triple of Traffic Signal Field Equipment → traffic detector data → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
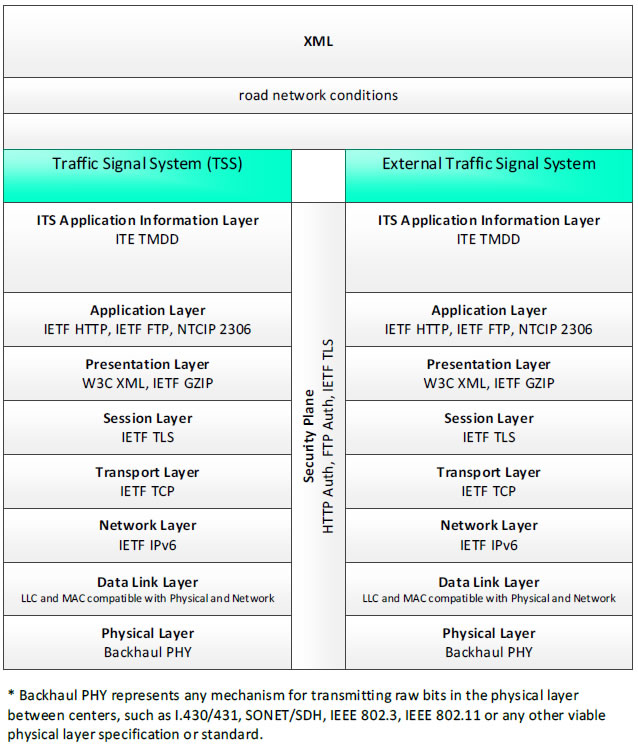
XML, road network conditions - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - HTTP Auth, FTP Auth, IETF TLS; 3) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C WML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 13. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the XML Triple of Traffic Signal System → road network conditions → External Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
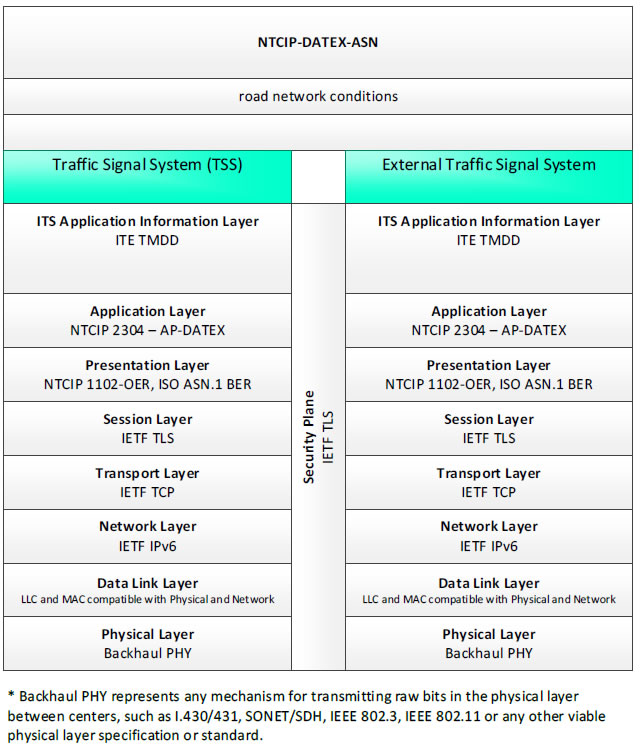
NTCIP-DATEX-ASN, road network conditions - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-Datex; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - IETF TLS; 3) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 14. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-DATEX-ASN Triple of Traffic Signal System → road network conditions → External Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
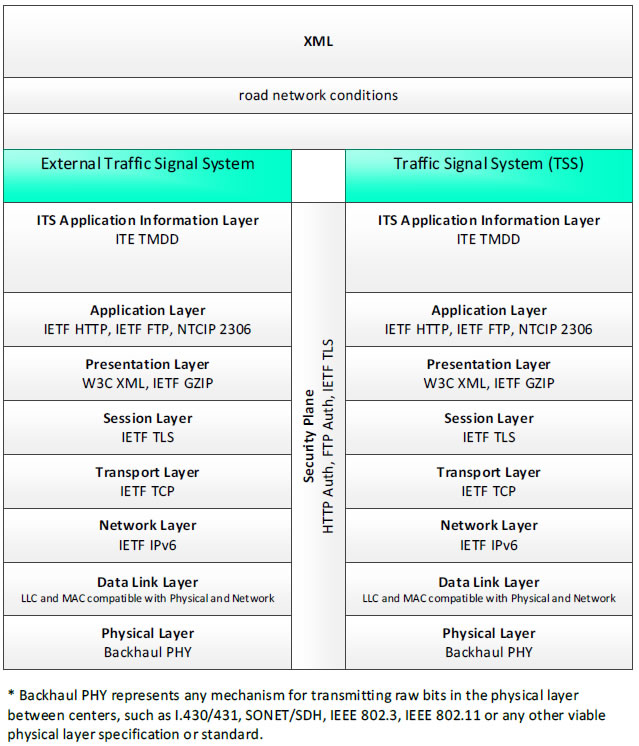
XML, road network conditions - 3 columns - 1) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C WML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - HTTP Auth, FTP Auth, IETF TLS; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 15. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the XML Triple of External Traffic Signal System → road network conditions → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
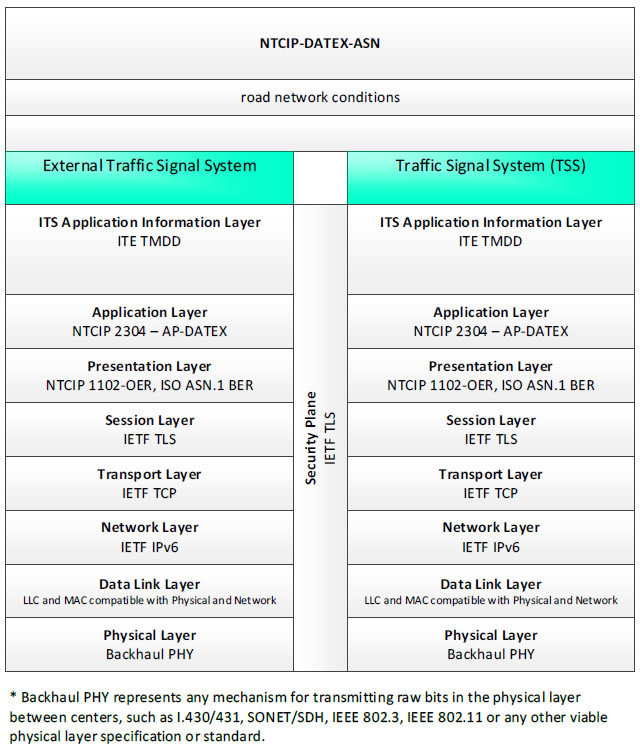
NTCIP-DATEX-ASN, road network conditions - 3 columns - 1) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - IETF TLS; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 16. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-DATEX-ASN Triple of External Traffic Signal System → road network conditions → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
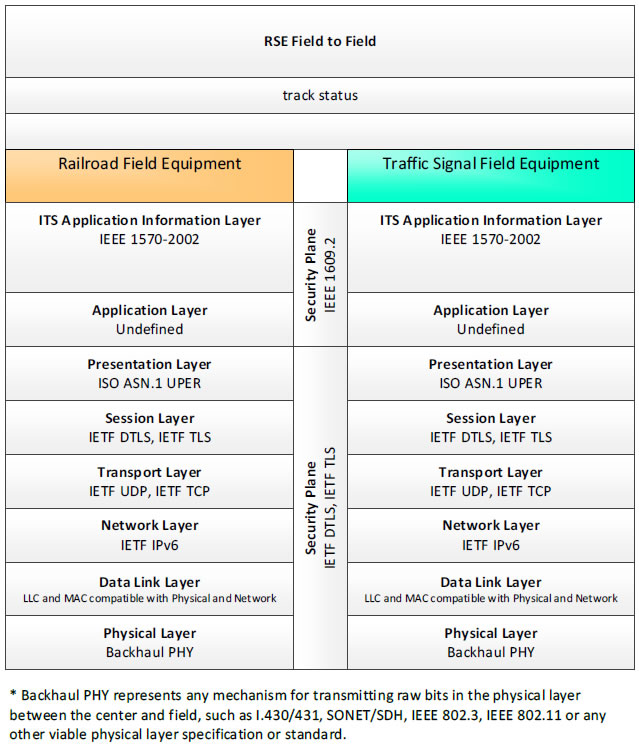
RSE Field to Field, track status - 3 columns - 1) Railroad Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - IEEE 1570-2002; Application Layer - Undefined; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 UPER; Session Layer - IETF DTLS, IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF UDP, IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - IETF DTLS, IETF TLS; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - IEEE 1570-2002; Application Layer - Undefined; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 UPER; Session Layer - IETF DTLS, IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF UDP, IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 17. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the RSE Field to Field Triple of Railroad Field Equipment → track status → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
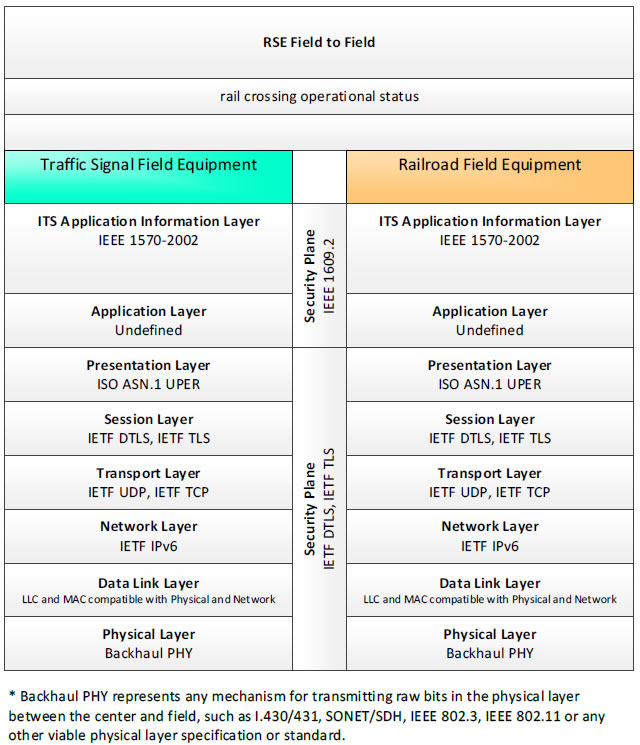
RSE Field to Field, rail crossing operational status - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - IEEE 1570-2002; Application Layer - Undefined; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 UPER; Session Layer - IETF DTLS, IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF UDP, IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - IETF DTLS, IETF TLS; 3) Railroad Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - IEEE 1570-2002; Application Layer - Undefined; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 UPER; Session Layer - IETF DTLS, IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF UDP, IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 18. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the RSE Field to Field Triple of Traffic Signal Field Equipment → rail crossing operational status → Railroad Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
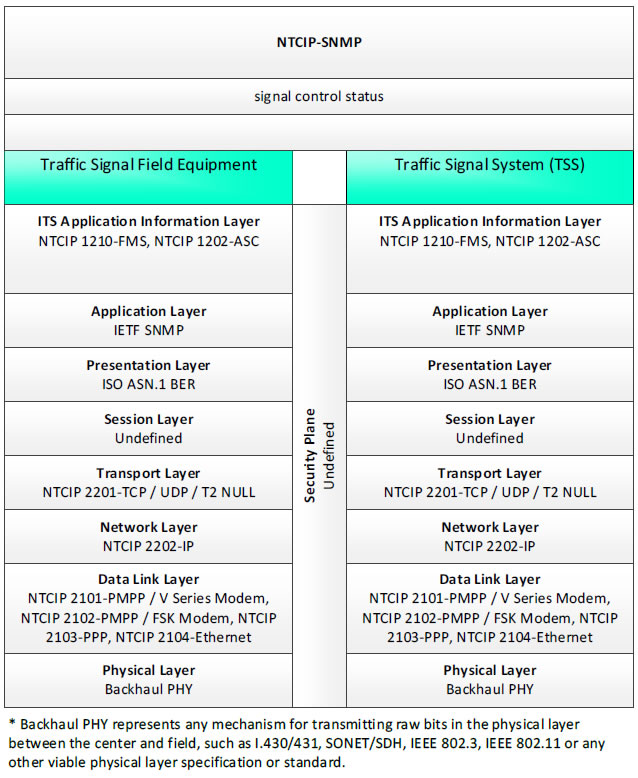
NTCIP-SNMP, signal control status - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2102-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 19. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-SNMP Triple of Traffic Signal Field Equipment → signal control status → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
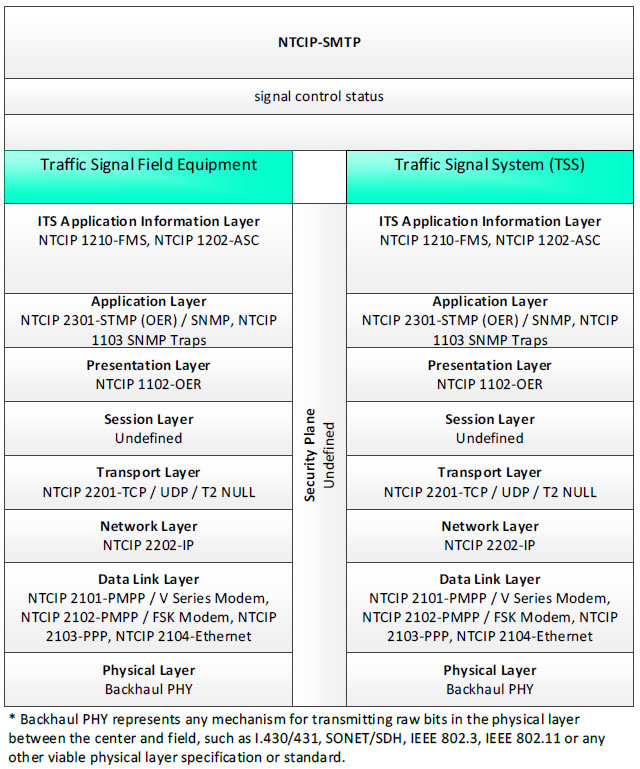
NTCIP-SMTP, signal control status - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 20. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-STMP Triple of Traffic Signal Field Equipment → signal control status → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
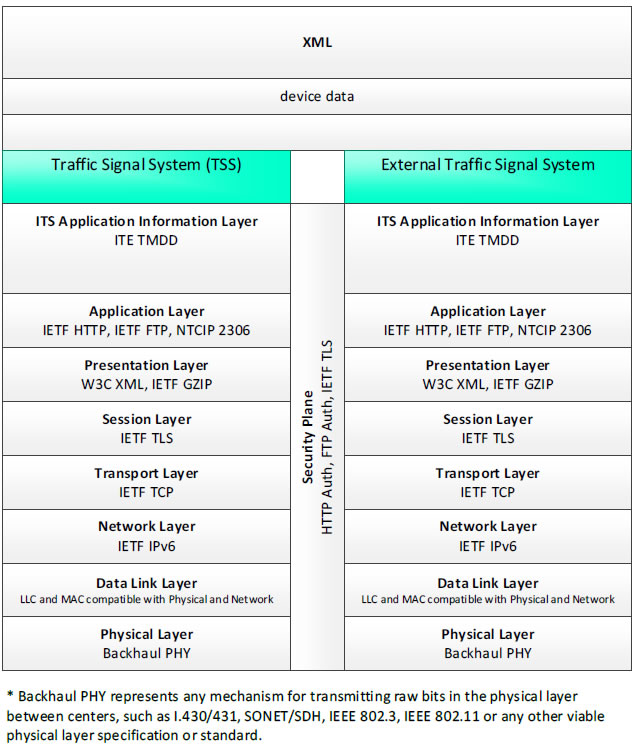
XML, device data - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - HTTP Auth, FTP Auth, IETF TLS; 3) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 21. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the XML Triple of Traffic Signal System → device data → External Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
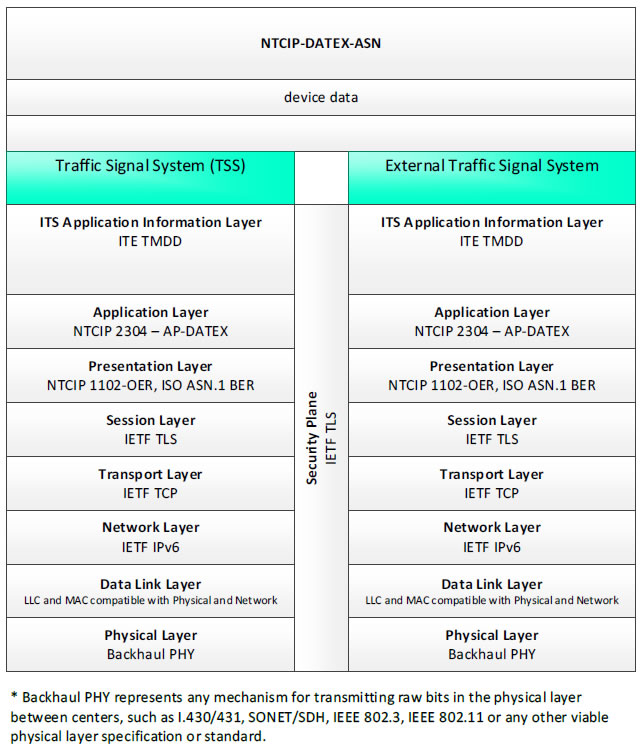
NTCIP-DATEX-ASN, device data - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - IETF TLS; 3) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 22. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-DATEX-ASN Triple of Traffic Signal System → device data → External Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
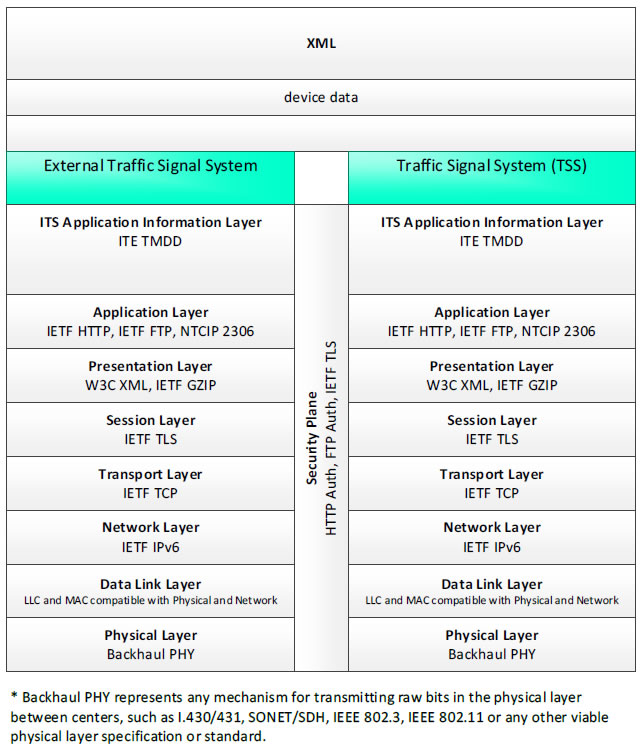
XML, device data - 3 columns - 1) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - HTTP Auth, FTP Auth, IETF TLS; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 23. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the XML Triple of External Traffic Signal System → device data → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
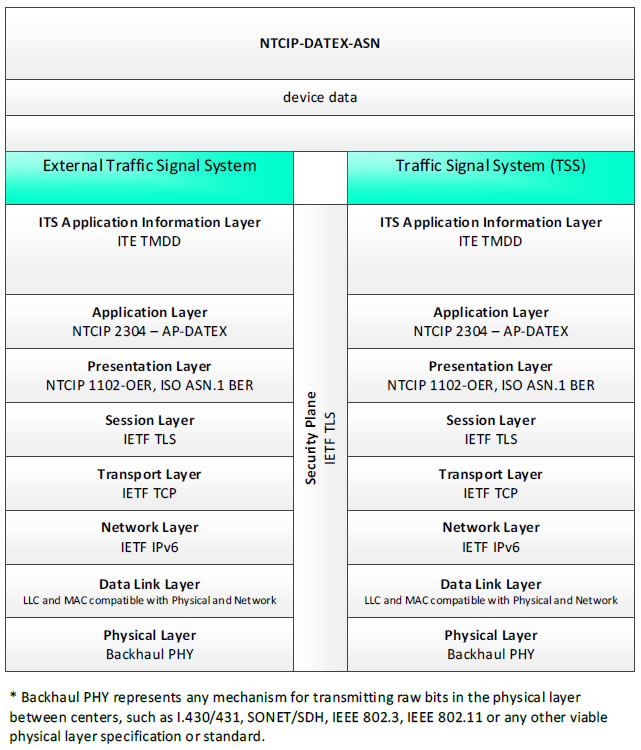
NTCIP-DATEX-ASN, device data - 3 columns - 1) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - IETF TLS; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 24. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-DATEX-ASN Triple of External Traffic Signal System → device data → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
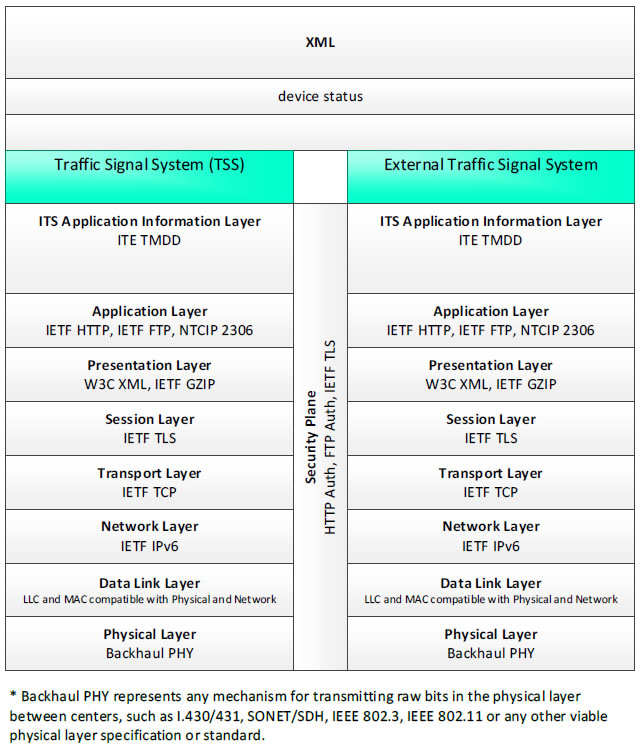
XML, device status - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - HTTP Auth, FTP Auth, IETF TLS; 3) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 25. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the XML Triple of Traffic Signal System → device status → External Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
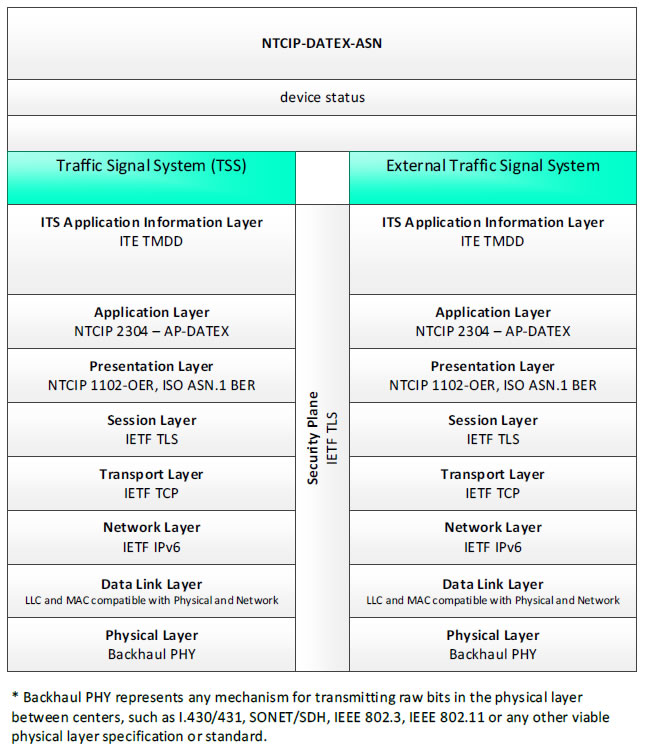
NTCIP-DATEX-ASN, device status - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - IETF TLS; 3) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN. BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 26. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-DATEX-ASN Triple of Traffic Signal System → device status → External Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
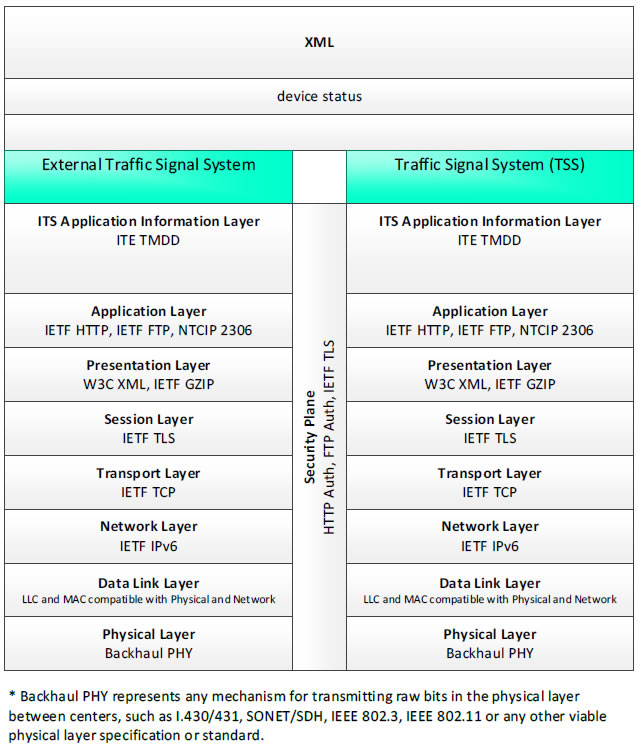
XML, device status - 3 columns - 1) Eternal Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - HTTP Auth, FTP Auth, IETF TLS; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 27. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the XML Triple of External Traffic Signal System → device status → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
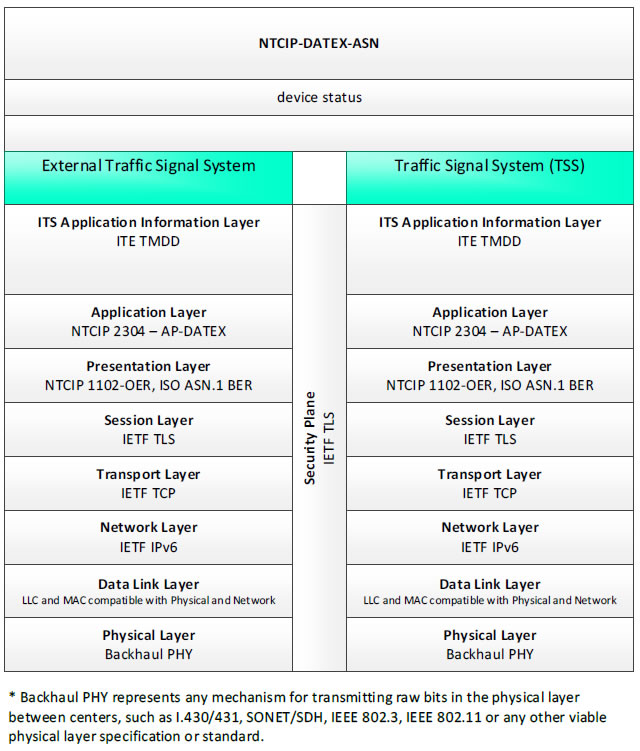
NTCIP-DATEX-ASN, device status - 3 columns - 1) Eternal Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - IETF TLS; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 28. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-DATEX-ASN Triple of External Traffic Signal System → device status → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
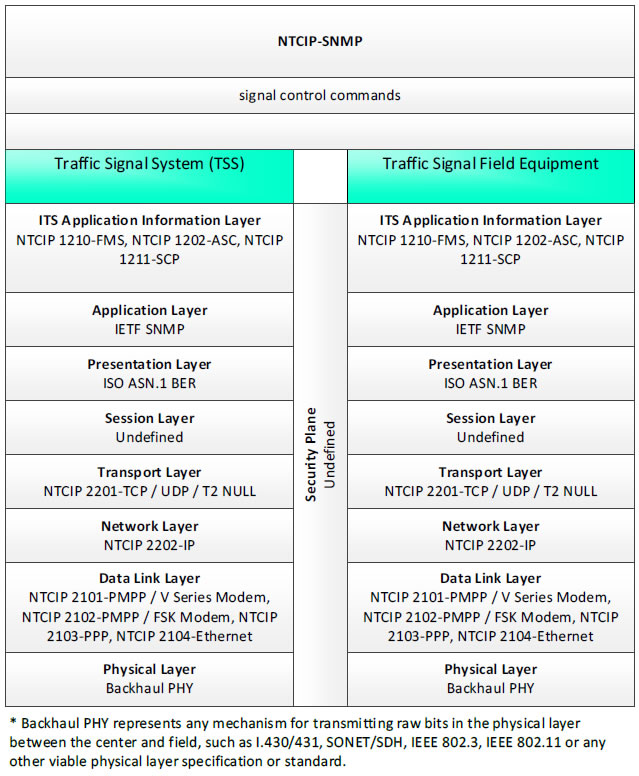
NTCIP-SNMP, signal control commands - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
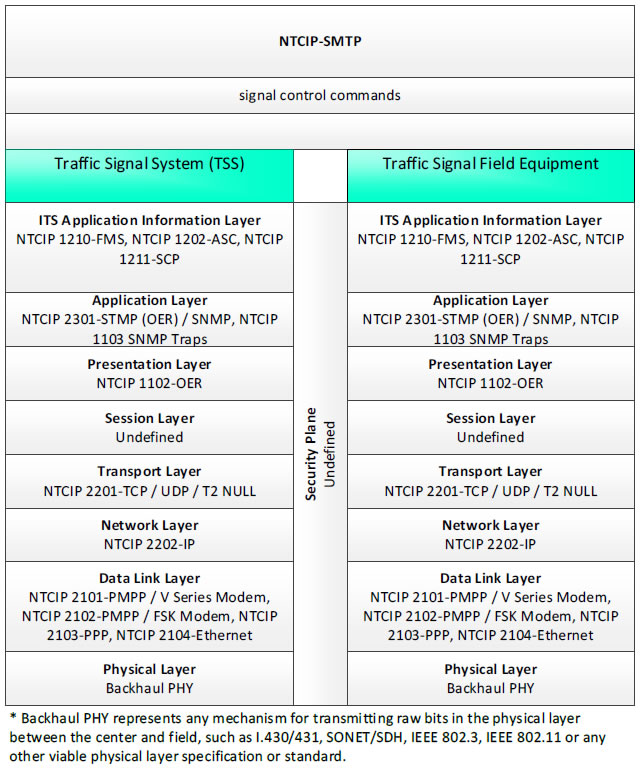
NTCIP-SNMP, signal control commands - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 30. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-STMP Triple of Traffic Signal System → signal control commands → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
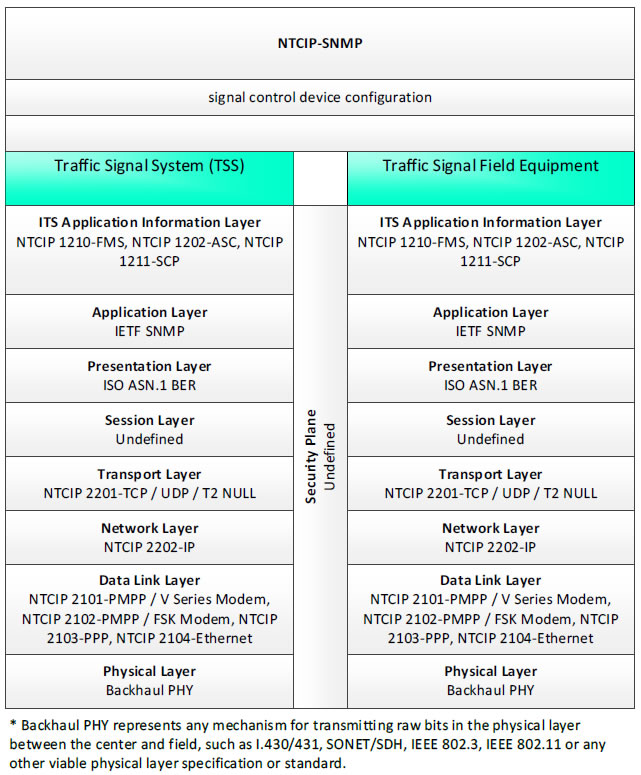
NTCIP-SNMP, signal control device configuration - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 31. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-SNMP Triple of Traffic Signal System → signal control device configuration → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
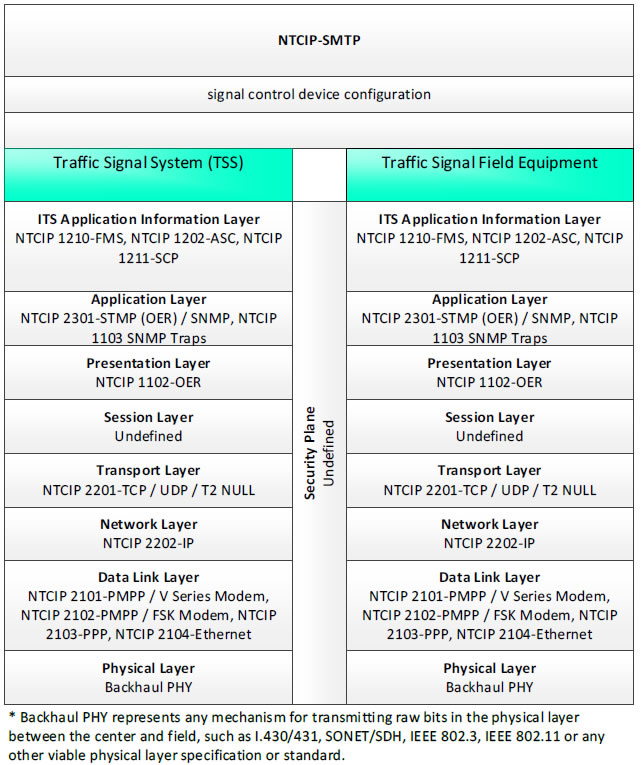
NTCIP-SMTP, signal control device configuration - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 32. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-STMP Triple of Traffic Signal System → signal control device configuration → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
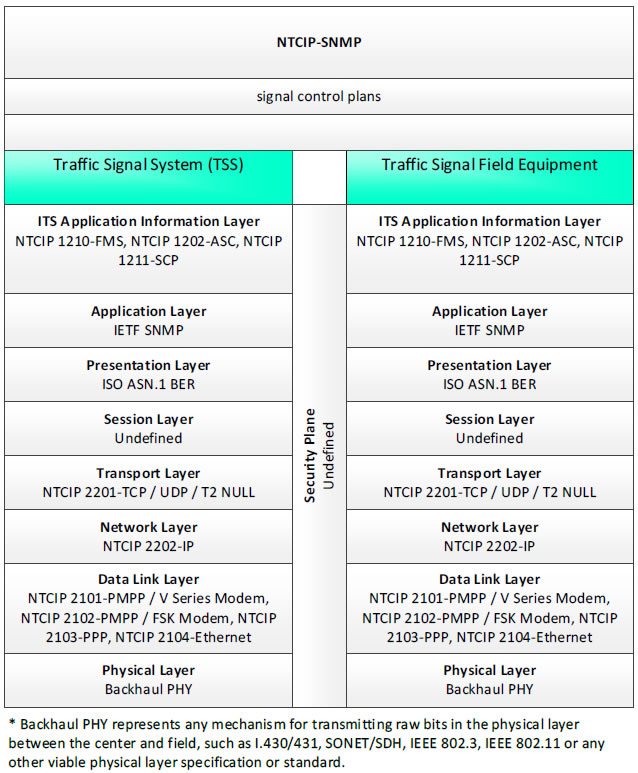
NTCIP-SNMP, signal control plans - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 33. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-SNMP Triple of Traffic Signal System → signal control plans → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
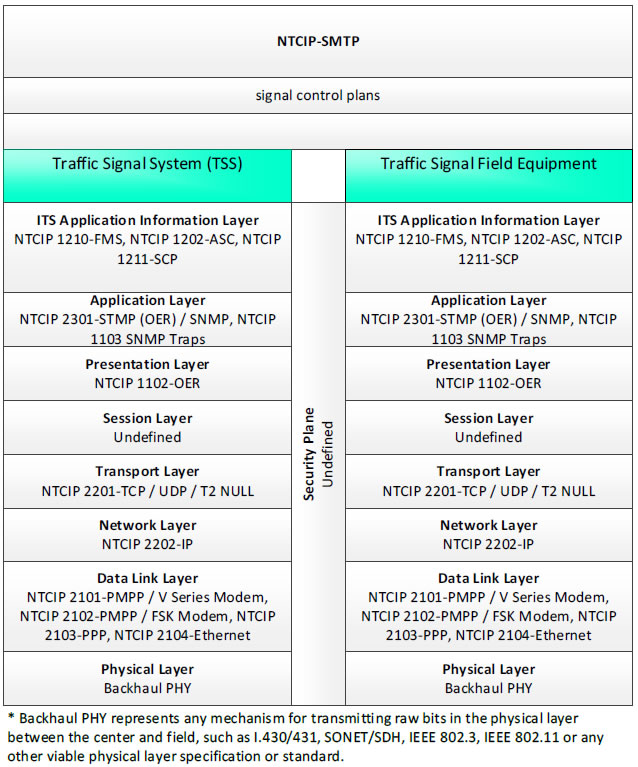
NTCIP-SMTP, signal control plans - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 34. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-STMP Triple of Traffic Signal System → signal control plans → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
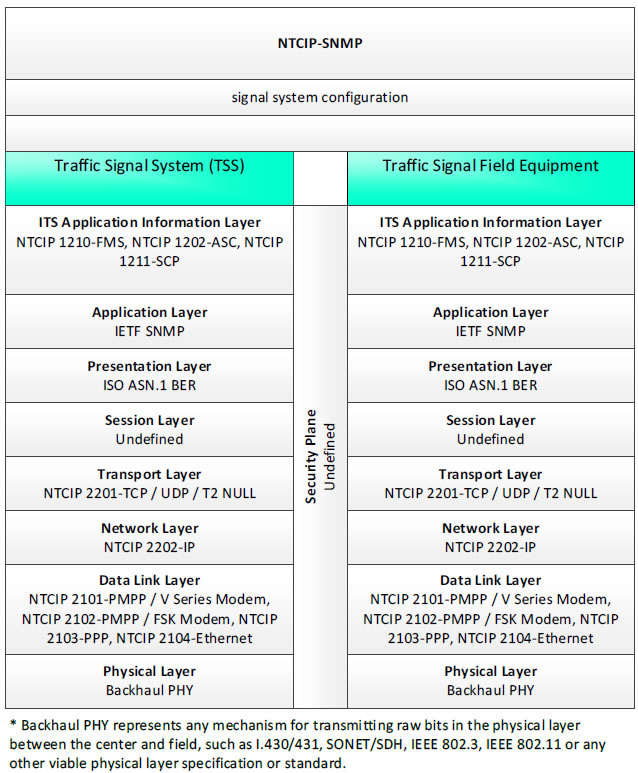
NTCIP-SNMP, signal system configuration - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 35. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-SNMP Triple of Traffic Signal System → signal system configuration → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
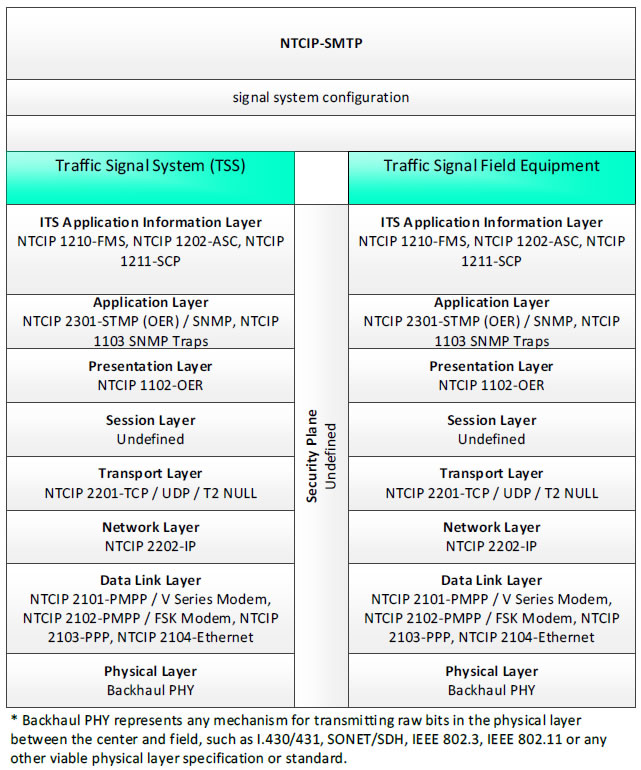
NTCIP-SMTP, signal system configuration - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 36. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-STMP Triple of Traffic Signal System → signal system configuration → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
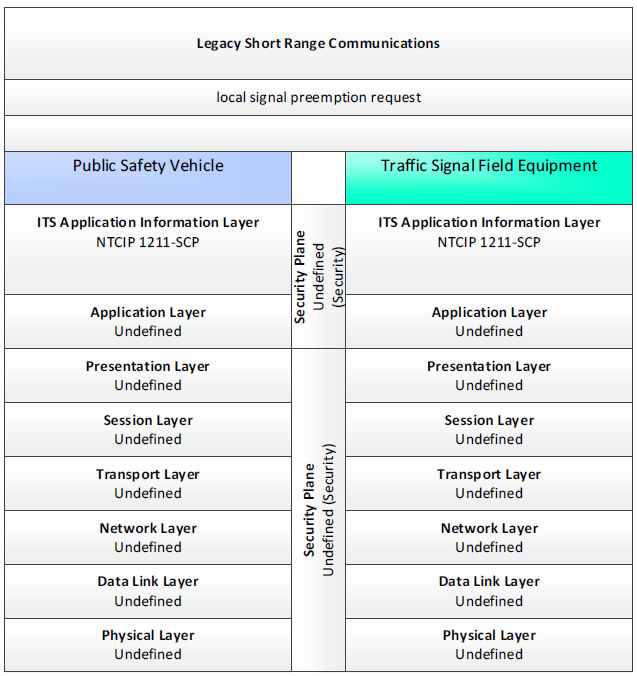
Legacy Short Range Communications, local signal preemption request - 3 columns - 1) Public Safety Vehicle - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - Undefined; Presentation Layer - Undefined; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - Undefined; Network Layer - Undefined; Data Link Layer - Undefined; Physical Layer - Undefined; 2) Security Plane - Undefined (Security); 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - Undefined; Presentation Layer - Undefined; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - Undefined; Network Layer - Undefined; Data Link Layer - Undefined; Physical Layer - Undefined.
Figure 37. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the Legacy Short Range Communications Triple of Public Safety Vehicle → local signal preemption request → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
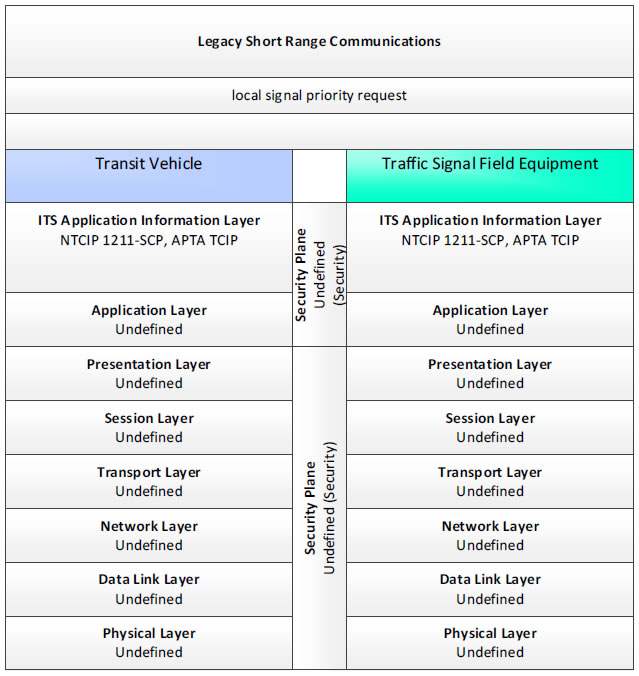
Legacy Short Range Communications; local signal priority request - 3 columns - 1) Transit Vehicle - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1211-SCP, APTA TCIP; Application Layer - Undefined; Presentation Layer - Undefined; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - Undefined; Network Layer - Undefined; Data Link Layer - Undefined; Physical Layer - Undefined; 2) Security Plane - Undefined (Security); 3) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1211-SCP, APTA TCIP; Application Layer - Undefined; Presentation Layer - Undefined; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - Undefined; Network Layer - Undefined; Data Link Layer - Undefined; Physical Layer - Undefined.
Figure 38. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the Legacy Short Range Communications Triple of Transit Vehicle → local signal priority request → Traffic Signal Field Equipment based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
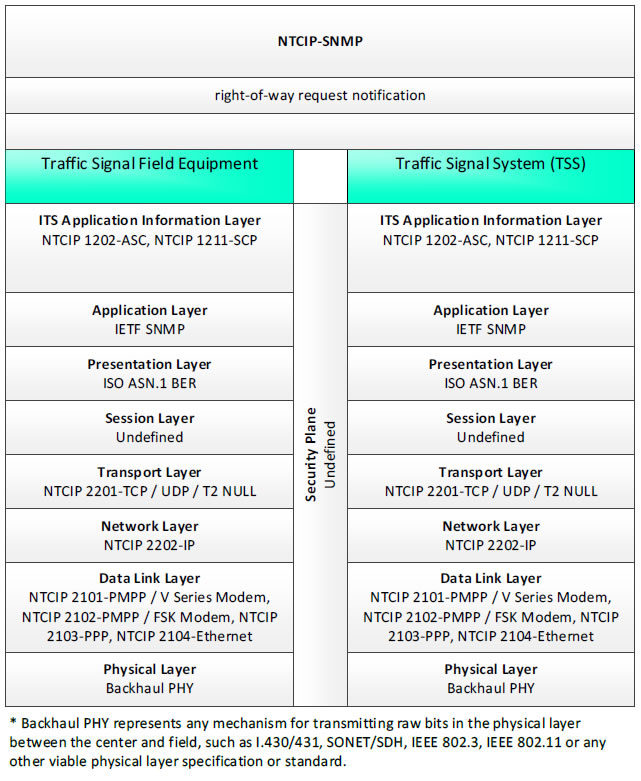
NTCIP-SNMP; right-of-way request notification - 3 columns - 1) Transit Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 39. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-SNMP Triple of Traffic Signal Field Equipment → local signal preemption request → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
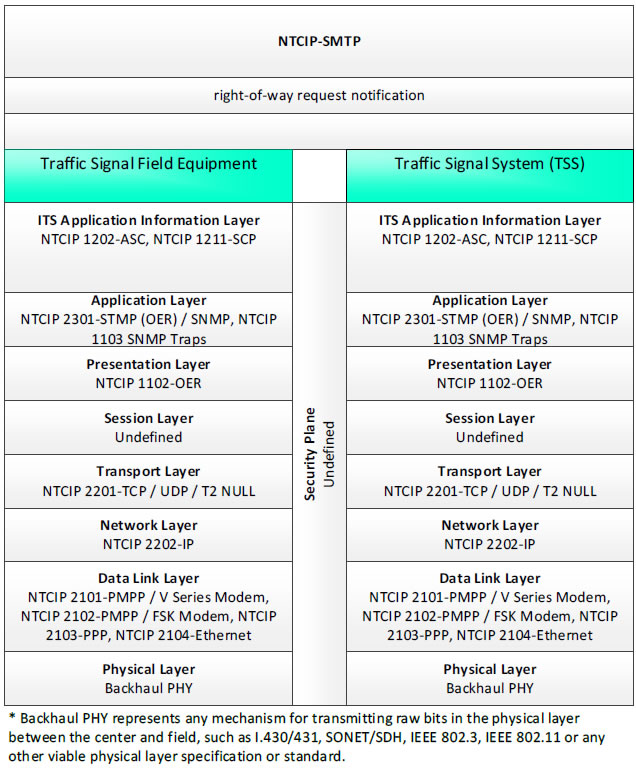
NTCIP-SMTP; right-of-way request notification - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined; 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1202-ASC, NTCIP 1211-SCP; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 40. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-STMP Triple of Traffic Signal Field Equipment → right-of-way request notification → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
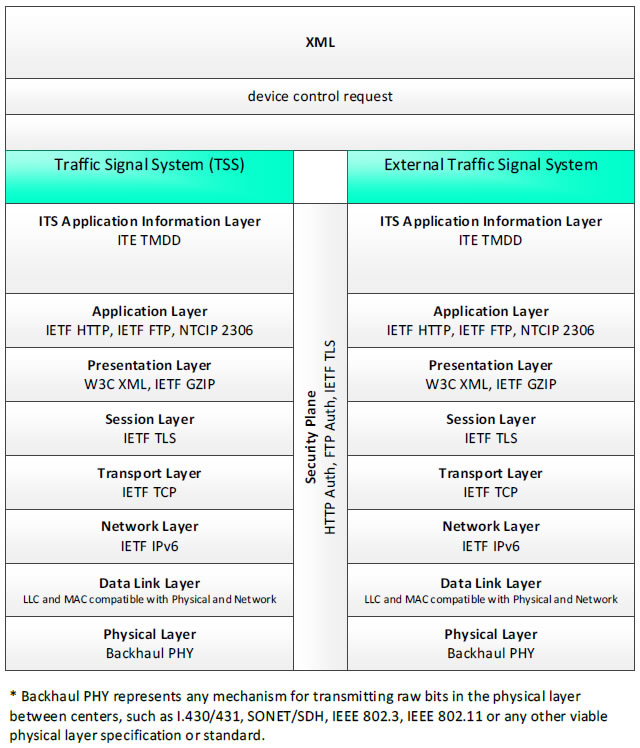
XML; device control request - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - HTTP Auth, FTP Auth, IETF TLS 3) External Traffic Signal System - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 41. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the XML Triple of Traffic Signal System → device control request → External Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
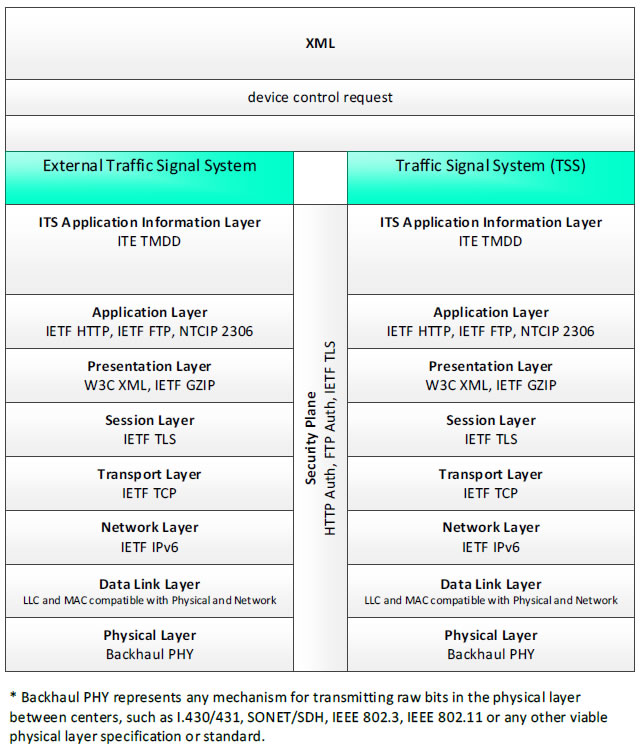
XML; device control request - 3 columns - 1) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - HTTP Auth, FTP Auth, IETF TLS 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - IETF HTTP, IETF FTP, NTCIP 2306; Presentation Layer - W3C XML, IETF GZIP; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 42. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the XML Triple of External Traffic Signal System → device control request → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
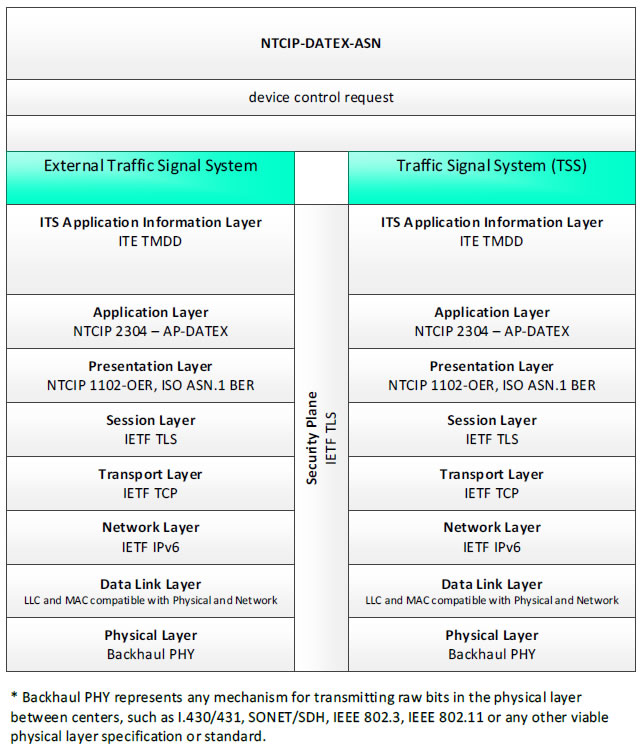
NTCIP-DATEX-ASN; device control request - 3 columns - 1) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - HTTP Auth, FTP Auth, IETF TLS 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304 - AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Network; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 43. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-DATEX-ASN Triple of External Traffic Signal System → device control request → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
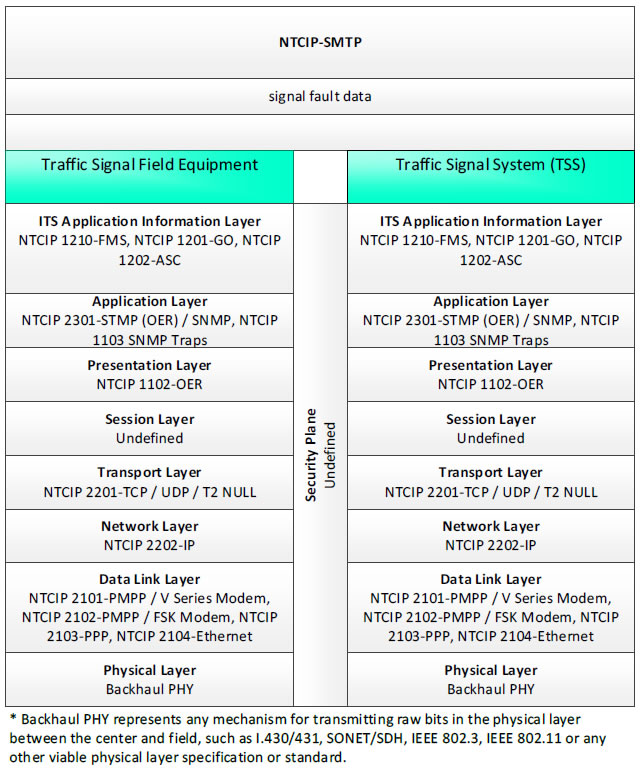
NTCIP-SMTP; signal fault data - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1201-GO, NTCIP 1202-ASC; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1201-GO, NTCIP 1202-ASC; Application Layer - NTCIP 2301-STMP (OER)/SNMP, NTCIP 1103 SNMP Traps; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 44. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-STMP Triple of Traffic Signal Field Equipment → signal fault data → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
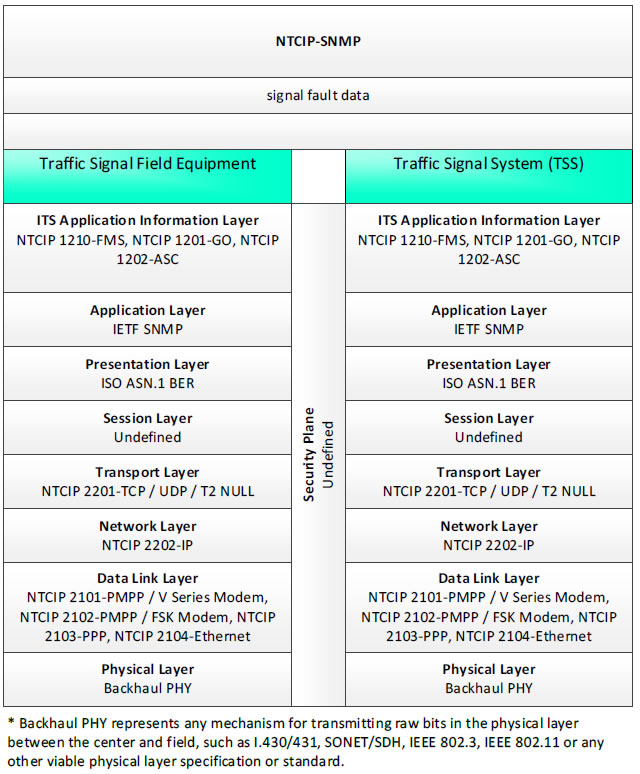
NTCIP-SNMP; signal fault data - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal Field Equipment - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1201-GO, NTCIP 1202-ASC; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - Undefined 3) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - NTCIP 1210-FMS, NTCIP 1201-GO, NTCIP 1202-ASC; Application Layer - IETF SNMP; Presentation Layer - ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - Undefined; Transport Layer - NTCIP 2201-TCP/UDP/T2 NULL; Network Layer - NTCIP 2202-IP; Data Link Layer - NTCIP 2101-PMPP/V Series Modem, NTCIP 2102-PMPP/FSK Modem, NTCIP 2103-PPP, NTCIP 2104-Ethernet; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 45. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-SNMP Triple of Traffic Signal Field Equipment → signal fault data → Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram
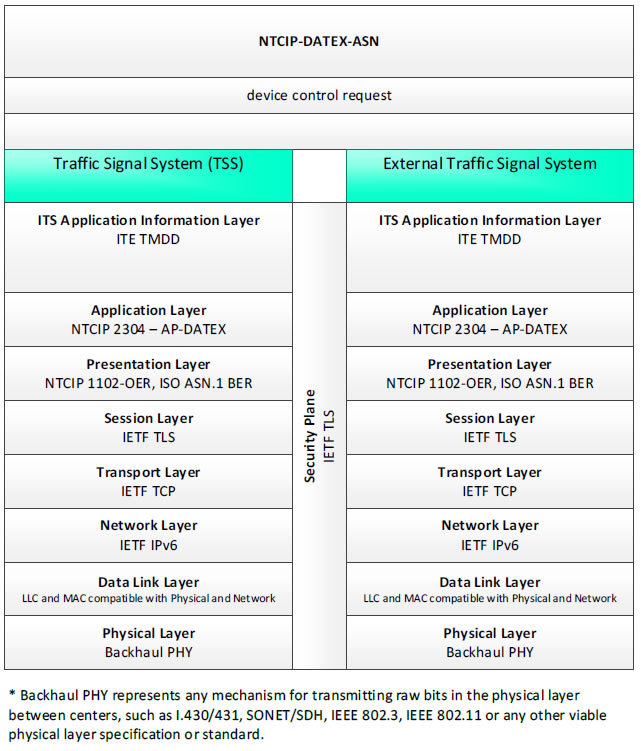
NTCIP-DATEX-ASN; device control request - 3 columns - 1) Traffic Signal System (TSS) - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304- AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Networked; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; 2) Security Plane - IETF TLS 3) External Traffic Signal System - ITS Application Information Layer - ITE TMDD; Application Layer - NTCIP 2304- AP-DATEX; Presentation Layer - NTCIP 1102-OER, ISO ASN.1 BER; Session Layer - IETF TLS; Transport Layer - IETF TCP; Network Layer - IETF IPv6; Data Link Layer - LLC and MAC compatible with Physical and Networked; Physical Layer - Backhaul PHY; * Backhaul PHY represents any mechanism for transmitting raw bits in the physical layer between the center and field, such as I.430/431, SONET/SDH, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.11 or any other viable physical layer or standard.
Figure 46. Communications Protocol Standards Example for the NTCIP-DATEX-ASN Triple of Traffic Signal System → device control request → External Traffic Signal System based on the CTSS Project Architecture Diagram